Excel’s SUM Function [inc 2 Examples & Troubleshooting]
Contents
The SUM Function quickly adds up numbers in a range of cells.
It’s simply how adding in Excel is handled!
It’s a simple and powerful tool, taught in our intro to Excel course.
SUM Function Details
| Available in: | All versions of Microsoft Excel |
| User Level: | Beginners |
| Inputs: | Range, Criteria, Sum_range |
| Output: | Sum of selected cells. Data Type: Number |
| Wildcards: | Supports “*” and “?” |
| Case Sensitive: | No, treats similar texts the same |
Where To Find The SUM Function
To find the SUM function and start adding cells in Excel, go to the top of the ribbon on your screen.
Click Formulas > Math & Trig, and scroll down to the SUM Function.
Pro Tip: You can also use AI tools to pick and generate formulas!

Using SUM With Other Data Types
SUM is a very precise function and will not work with data types other than numbers.
To get intended results, you will need to use numbers.
Check out the below example to see what happens when you use dates!
Date Data:
Excel treats dates as numbers.
Because of this, you will get unintended outcomes when adding up dates.
Simple Example
Imagine you want to add up your daily expenses.
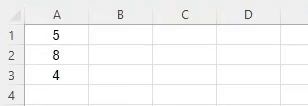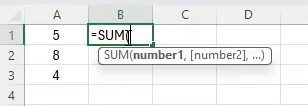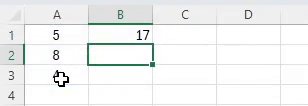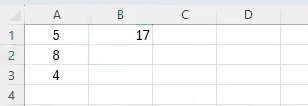
Select the cells with your expense amounts, then use the SUM function:
=SUM(A2:A5)This formula adds up the values from cell A2 to A7.
Advanced Example
Let’s combine SUM with IF to sum only certain expenses.
Suppose you only want to add expenses over £50:
=SUMIF(A2:A5,">=50",A2:A5)This formula sums values in A2:A5 that are greater than $50.
You can even use the SUM function to create a data model in Excel!
Troubleshooting & Errors
So what are some common errors when using the SUM Function in Excel?
Error 1: #VALUE! Error
Cause: Mixing data types like text and numbers in the sum range.
Solution: Ensure all cells in the range contain numeric values.
Error 2: Unexpected Results with Dates
Cause: Summing date-formatted cells directly.
Solution: Convert dates to numbers using DATEVALUE before summing.
What Is The SUM Function Useful For?
The SUM function is a fundamental tool to Excel, and it can be used for plenty of work.
| 1. Data Validation: | Ensures data integrity by checking the sum of a range against expected totals. |
| 2. Basic Statistical Analysis: | Quickly calculates total values, an essential step in many statistical methods. |
| 3. Budget Tracking: | Adds up expenses or income, helping in personal or business budget management. |
You can also use SUM alongside the TRIM Function to clean and analyse your data!
Similar Useful Functions
Other functions similar to the Excel value function that are easy to use include:
- COUNT: Counts the number of cells in a range rather than adding them.
- AUTOSUM: AutoSum is a button, not a function, but will generate your SUM formula for you!
- SUMIF: Adds cells based on a specified condition
Taking advantage of these functions together will help build your Excel skills overall, and make you a well-rounded user!
Conclusion
The SUM function in Excel is a fundamental tool for anyone working with data.
It’s simple enough for beginners but can be combined with other functions for more complex tasks.
Understanding SUM is key to efficient data management and analysis in Excel.